Cloud : data protection
The Cloud is nowadys a key tool for CIOs/IT Services Director, thanks to its flexibility, the cost reduction made and time-to-market improvements. 85% of companies in the private sector have adopted it (IDC 2016 figures).
For companies that have their business application in the Cloud :
- 90% believe the Cloud enables them to innovate faster
- 73% think the Cloud helps them to keep their existing clients
- 76% think the Cloud helps them to gain new clients
Security is obviously the main concern identified by decision makers as to the use of Cloud in business context (source State of Cloud Report 2016 - BetterCloud).
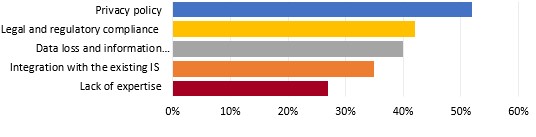
The security of the Cloud, a key element
According to a 2017 study for LinkedIn among 2,200 companies using the Cloud :
- 198 had a security incident on the Cloud
- 264 can not reveal anything
- 462 don’t know they are using the Cloud and show a lack of knowledge
- 1210 didn’t have any problems
69 days on average were needed to find the security incident, 7 days to resolve it and 43 days for the investigations to be done.
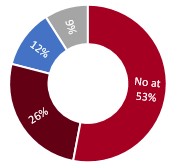
Nevertheless, the implementation of the security can have a very important impact on the budgets, the delivery delays of the solutions and the agility. These three criteria helps us see the advantages of the Cloud over the software On Premise.
.You need to be extremely careful on the perimeter and the levels of security desired, at the risk that the ROI of a use of the Cloud is not what you were expected.
The steps of securing the Cloud
1 Identify your data and their constraints
An essential phase is the knowledge of the data of the company and their classification by level of confidentiality. This step will allow you to know which data can be outsourced, under which conditions and which will remain On Premise.
The legal constraints and laws may change, according to the type of data (personal, financial, industrial, commercial, public data, etc.). The data can also be subjected to different regulations (GDPR, CNIL, ANSSI, PCI-DSS, avoid the American Patriot Act,etc.). These constraints can then impose the choice of your Cloud Provider (eg French with a datacenter in France).
2 Define the type of Cloud to use
Depending on the data to be outsourced and their associated constraints, several types of Cloud are available: public, private and hybrid (mix between public and private Cloud). The use of an hybrid Cloud will limit the efforts of security for the public data (public Cloud), secure the more confidential data (private data), while allowing to keep a link between the two worlds.
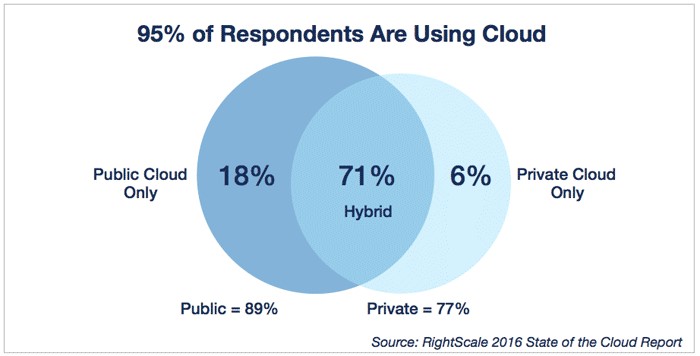
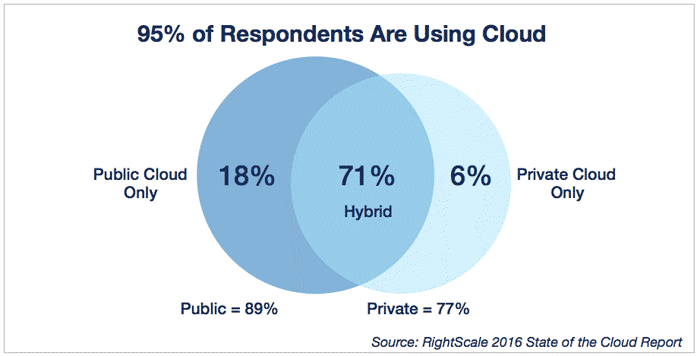
Type of Cloud used in companies - Source RightScale 2016, study among 1060 companies
3 Train your developers
The implementation of the Agiles and DevOps structures broadened the prerogatives of the development teams and helps with the controls. Train your developers to secure their code from the start can greatly reduce the risk later (eg Open Web Application Security Project).
4 Study the technical solutions to be used
- Network partitioning
- Tooling and Application Segmentation
- Separation of applications and databases
- Stream encryption
- Dara encryption
- North-South and East-West Firewall
- WAF (Web Application Firewall)
- Reverse Proxy
- Autohealing
- Administrators strong multifactor authentication
- IAM (Identity Access Management) and SSO (Single Sign On)
- SIEM to correlate and analyze logs
- Deployment of security updates and patches
- Intrusion Detection/Prevention System (IDS)
- DDOS protection
- Supervision
- Backups
- PCA and DRP
- Properly identify its data and constraints
- Include from the beginning of discussions the Security Department and the developers
- Take advantage of the Cloud to promote DevOps
- Do not seek to secure everything
- Do not neglect the security budget needed to use the Cloud
- Do not limit a cloud migration to technical operations
